
I. Product Definition and Structural Features
A hexagon bolt with a hole in the head is a type of fastener featuring a hexagonal head and an axial through-hole. The hole in the head is designed to allow flexible connectors such as ropes or lock pins to pass through, enabling additional fixing or suspension functions. The product is classified into precision grades A and B, with Grade A offering higher precision and being suitable for applications requiring strict dimensional tolerances, while Grade B is intended for general industrial use. The standard covers a nominal thread diameter range from 5 mm to 48 mm, including variants such as thin shank and fine thread types, providing a comprehensive fastening solution.
II. Typical Application Scenarios
This bolt is widely used in engineering fields requiring secondary fixation, such as:
-
Power Facilities: Used for fixing stay wires on high-voltage transmission towers, where the hole in the head connects to steel cables to enhance stability.
-
Construction Engineering: In steel structure connections, it can be used with split pins to prevent bolt loosening and improve seismic performance.
-
Mechanical Assembly: Suitable for components requiring suspension or traction, such as hoisting equipment and conveyor systems.
III. Core Dimensional Parameters
The standard specifies the geometric dimensions of the bolt in detail to ensure interchangeability among products from different manufacturers. Key parameters include:
-
Thread Specifications: Ranging from M5 to M48, with each diameter corresponding to specific thread lengths and pitches.
-
Head Dimensions: Width across flats (S), height (k), and hole diameter (d1) of the hexagon head. For example, an M10 bolt has a head width across flats of 17 mm and a hole diameter of 3.2 mm.
-
Length Range: Thread lengths vary from 16 mm to 300 mm depending on the diameter, meeting diverse assembly requirements.
Dimensional data is categorized into preferred and non-preferred specifications to optimize supply chain management.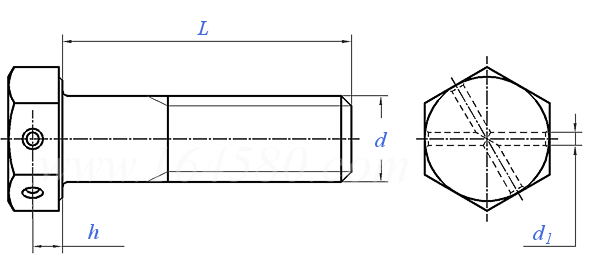
IV. Materials and Mechanical Properties
-
Material Selection: Primarily made from carbon steel or alloy steel, balancing strength and cost-effectiveness.
-
Performance Grades: The standard has removed the outdated 9.8 grade and introduced strength grades better suited to modern engineering needs, such as 8.8 and 10.9 grades, with tensile strengths of 800 MPa and 1000 MPa, respectively.
-
Surface Treatment: Processes such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, or Dacromet coating are recommended to enhance corrosion resistance for outdoor or humid environments.
V. Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
-
Process Highlights: Includes cold forging, thread processing (rolling or cutting), head drilling, and heat treatment (quenching and tempering).
-
Inspection Rules: Type testing and sampling inspections are conducted, covering dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties (such as tensile testing), and surface defect detection.
-
Marking Requirements: Each product must be marked with specifications, performance grade, and manufacturer code to ensure traceability.
VI. Standard Updates and Technical Improvements
Compared to the 1988 version, the 2020 edition includes several optimizations:
-
Structural Optimization: Dimensional tables are divided into preferred and non-preferred specifications, simplifying the selection process.
-
Performance Upgrades: Introduces higher strength grades to meet the lightweight requirements of modern equipment.
-
Reference Integration: Explicitly references standards such as GB/T 5782 (General Technical Requirements for Bolts) and GB/T 5278 (Pin Hole Dimensions), forming a collaborative standard system.
